Multicast Configuration
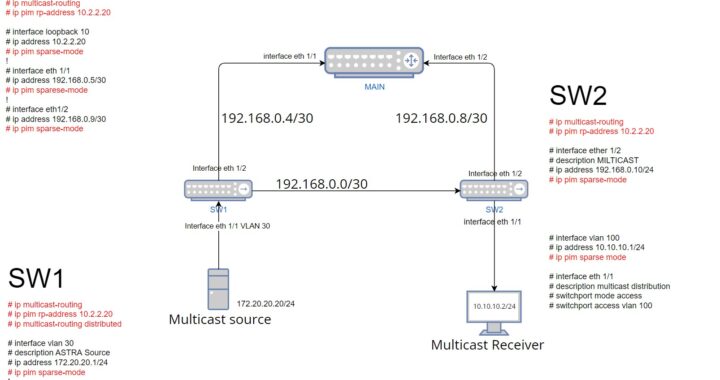
Configuring Multicast using PIM-SPARSE MODE and static RP configuration. Bellow is attached the scheme that we will configure the Multicast on 1 Router (that we are using as RP) and 2 L3 Switches (one of them is the source and one of them is the server).
Multicast is on top if IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol: is a dynamic route update protocol used between routers that run on TCP/IP hosts within a single autonomous system, the L3 devices uses this protocol to exchange the information about IP Routes.), that means without unicast IP Routing, Multicast will not work. The fist step is enabling the Multicast by command #ip multicast-routing (on routers) on switches you need (#ip multicast-routing distributed) or if the switches are cisco nexus user #feature pim.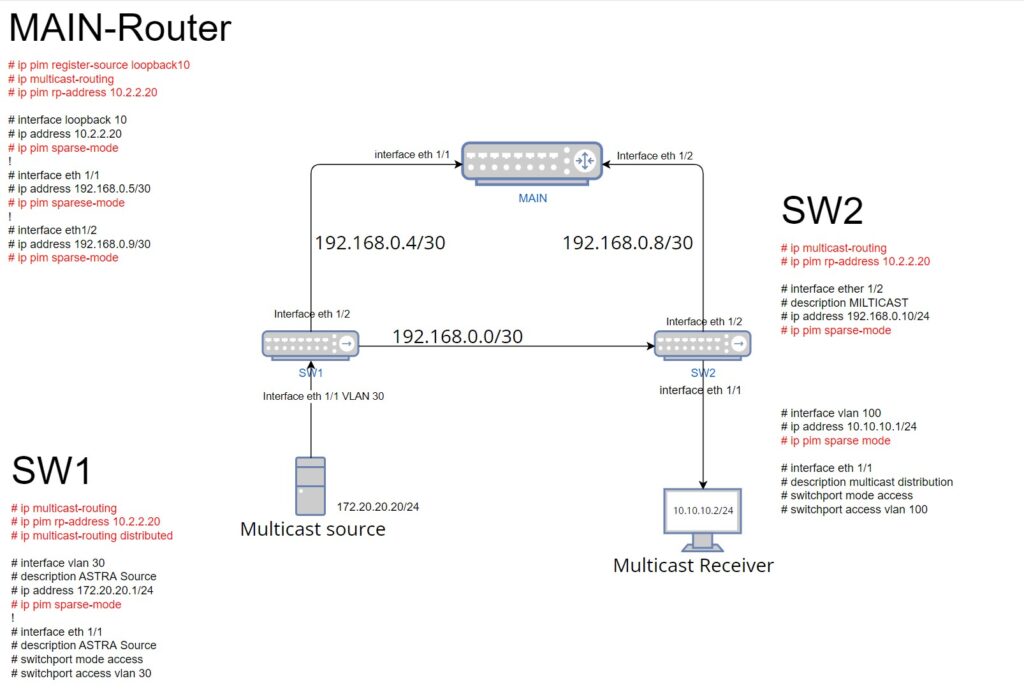
On layer 3 interfaces enable PIM (ip pim sparse-mode). In our case we need to apply on these interfaces (MAIN(loopback10, interface 1/1, interface 1/2), SW1(vlan30, ethernet1/1), SW2(ethernet1/2, vlan100)).
Next, configure RP address (RP is a router that announces itself that it wants to be an RP for the network. It does so by sending RP announcement packets to the 224.0. 1.39 multicast address) by the CLI command: #ip pim rp-address 10.2.2.20(in our case). This command should be written on every L3 devices that a network has(in our case in one router and two switches). In the scheme the MAIN router is a RP and we are using loopback interface as RP interface because it is the last interface that can do DOWN. After configuring rp-address we can check with #show ip pim rp mapping.
If there is no multicast application, there is a way that multicast can be tested by configuring:
#ip igmp join-group x.x.x.x (in our case on SW2 and interface ethernet 1/1 where the multicast receiver is connected)
To check if the multicast is seen by RP device do the command:
#show ip mroute
If there is S or G entry that means that Source to RP multicast is working.
With this command you can check all streams that are currently available.
If there is no stream available that means one there is an issue:
1. Receiver LHR (last hop router) to RP multicast is not available.
2. PIM is not properly enable or missconfigured
to troubleshot it you can use the command:
#mtrace {RP address}
#ping {source to RP & receiver to RP}
By using “ip pim spt-threshold infinity” command you can force not to switch over to shortest path.